Review and Unification of Current Unsupervised Domain Adaptation Methods
📅 Jul. 2020 - Nov. 2020 • 📄 Report

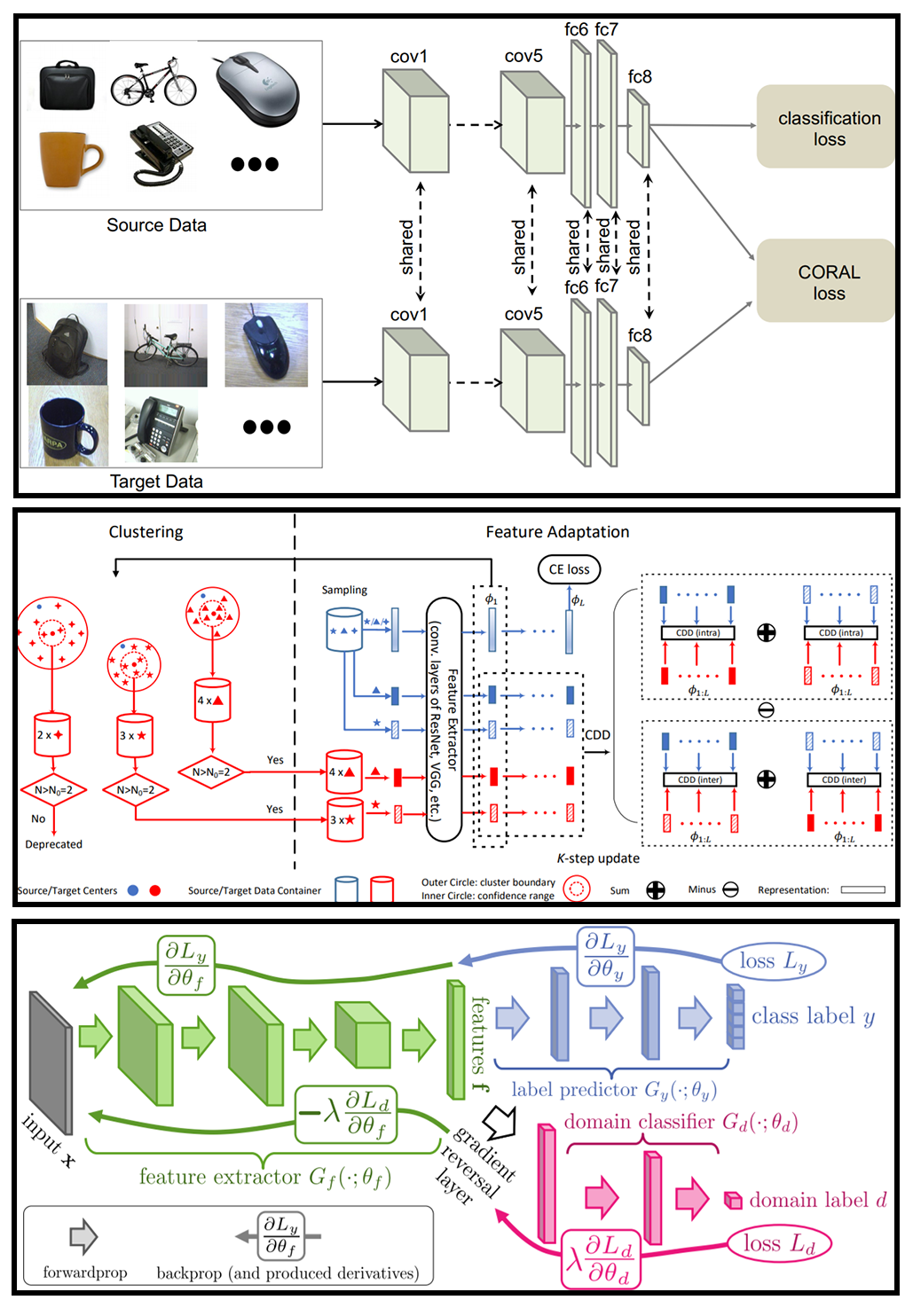
In supervised machine learning, a common paradigm is to use labeled data (the “training set”) to learn the weights of some model, and deploy it to unseen data at test time. Unfortunately, this is not always realistic in practice, because labeled data can be hard to obtain. Thus, we often find ourselves in a situation where we don’t have labeled data in the distribution we’re actually interested in (called the test distribution). In the test distribution, we only have unlabeled data. However, we do have labeled data in a similar distribution (called the target distribution). Note that there might be a gap between these two domains, and that some adaptation needs to occur for optimal performance.
In this project a survey of current methods in the unsupervised domain adaptation literature is performed, and a unified taxonomy is proposed to generalize the methods within one framework. A critical analysis is also taken at Contrastive Adaptation Network (CAN), one of the state-of-the-art method which utilizes psuedolabels. Recommendations are made with regards to CAN, to further improve performance beyond what is stated by the original authors. For details, please refer to the full report.